Architecture & Design
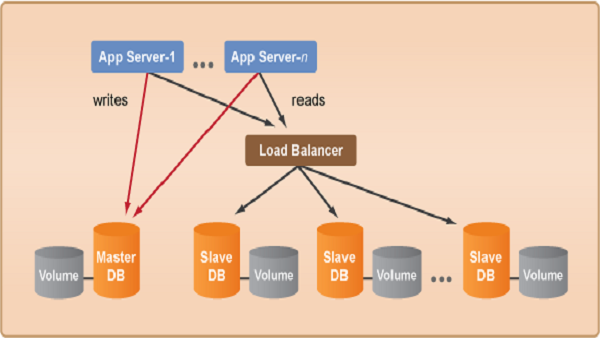
Cloud computing is one of the boons of technology, making storage and access of documents easier and efficient. For it to be reliable, the AWS cloud architecture need to be impeccable. It needs to be reliable, secure, high performing and cost efficient. A good AWS cloud architecture design should take advantage of some of the inherent strengths of cloud computing elasticity, ability to automate infrastructure management etc. Your AWS Cloud architecture design needs to be well thought out because it forms the backbone of a vast network. It cannot be arbitrarily designed.
Build using a structured approach
Strategies to help you compare your workload against our best practices, and obtain guidance to produce stable and efficient systems so you can focus on functional requirements.
1: Operational Excellence
The operational excellence pillar focuses on running and monitoring systems to deliver business value, and continually improving processes and procedures. Key topics include managing and automating changes, responding to events, and defining standards to successfully manage daily operations.
2: Security
The security pillar focuses on protecting information & systems. Key topics include confidentiality and integrity of data, identifying and managing who can do what with privilege management, protecting systems, and establishing controls to detect security events.
3: Reliability
The reliability pillar focuses on the ability to prevent, and quickly recover from failures to meet business and customer demand. Key topics include foundational elements around setup, cross project requirements, recovery planning, and how we handle change.
4: Performance Efficiency
The performance efficiency pillar focuses on using IT and computing resources efficiently. Key topics include selecting the right resource types and sizes based on workload requirements, monitoring performance, and making informed decisions to maintain efficiency as business needs evolve.
5: Cost Optimization
Cost Optimization focuses on avoiding un-needed costs. Key topics include understanding and controlling where money is being spent, selecting the most appropriate and right number of resource types, analyzing spend over time, and scaling to meet business needs without overspending.